# 二叉树递归遍历
二叉树是一种常见的数据结构,其节点最多有两个子节点:左子节点和右子节点。在对二叉树进行遍历时,我们有三种常见的方式:
- 前序遍历(Pre-order Traversal): 任何子树的处理顺序都是,先头节点、再左子树、然后右子树
- 中序遍历(In-order Traversal): 任何子树的处理顺序都是,先左子树、再头节点、然后右子树
- 后序遍历(Post-order Traversal): 任何子树的处理顺序都是,先左子树、再右子树、然后头节点
目标
- 深入理解二叉树结构: 通过练习遍历算法,可以更深入地理解二叉树的结构和特性,包括根节点、左右子节点的关系等。
- 解决相关问题: 二叉树的遍历算法常常用于解决与二叉树相关的问题,如查找特定节点、计算树的高度、检测树是否平衡等。
- 提高编程技能: 练习二叉树的遍历算法可以提高编程能力,包括递归算法的理解和应用、对数据结构的熟练运用等。
- 应用于其他领域: 二叉树的遍历算法不仅局限于数据结构和算法领域,还可以应用于其他领域,如图像处理、编译器设计等。
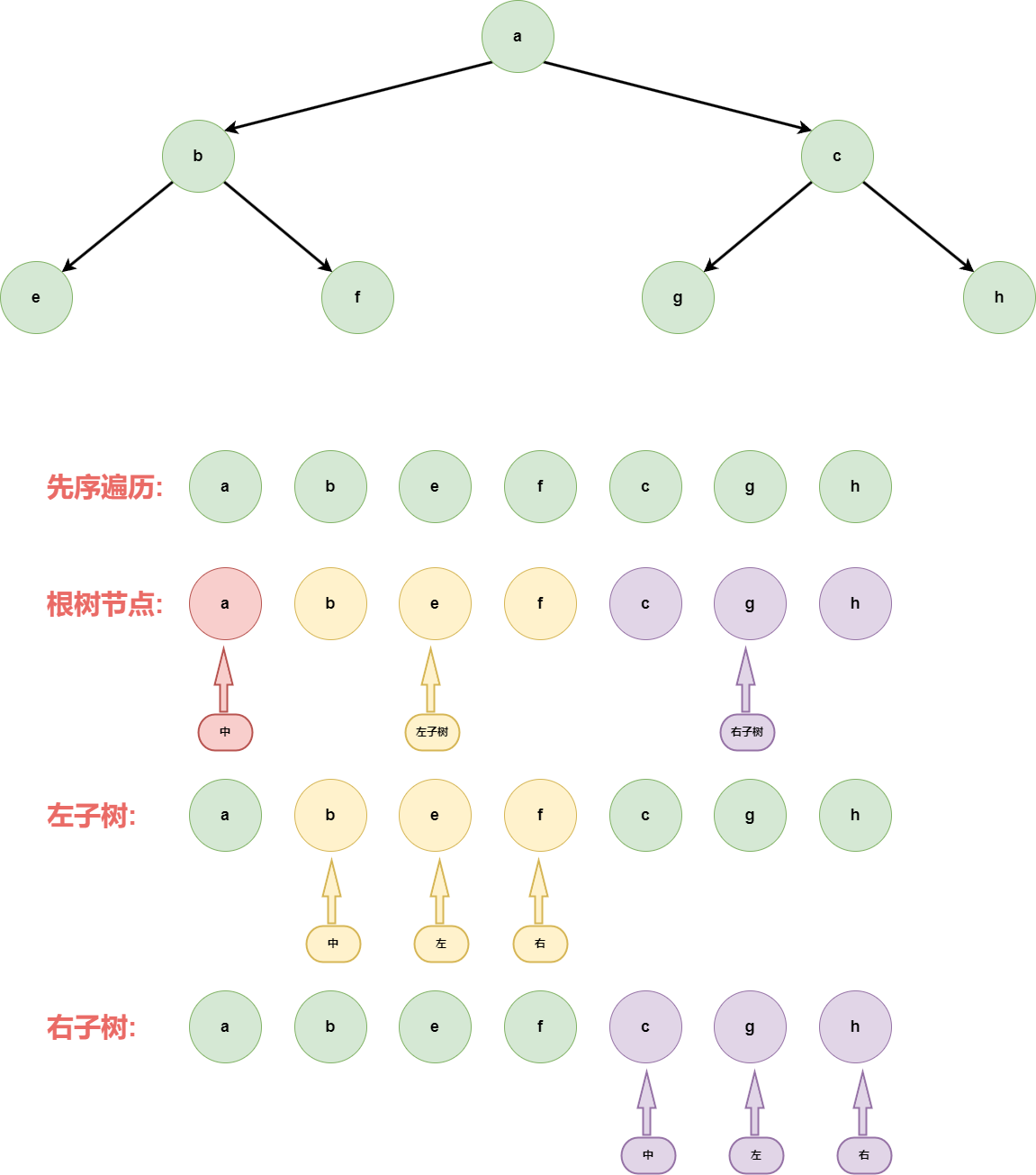
# 先序遍历
**前序遍历(Pre-order Traversal):**任何子树的处理顺序都是,先头节点、再左子树、然后右子树
代码实现
package binary_tree
import "fmt"
type TreeNode struct {
Value string
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
}
func PreTraversal(root *TreeNode) { // 先序遍历树节点
if root == nil {
return
}
fmt.Printf("%s ", root.Value) // 先处理自身
PreTraversal(root.Left) // 再先序遍历自身左子树
PreTraversal(root.Right) // 最后先序遍历自身右子树
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
测试
package binary_tree
import "testing"
func TestPreTraversal(t *testing.T) {
root := &TreeNode{Value:"a"}
root.Left = &TreeNode{Value:"b"}
root.Right = &TreeNode{Value:"c"}
root.Left.Left= &TreeNode{Value:"e"}
root.Left.Right= &TreeNode{Value:"f"}
root.Right.Left= &TreeNode{Value:"g"}
root.Right.Right= &TreeNode{Value:"h"}
PreTraversal(root)
}
/* 测试结果
=== RUN TestPreTraversal
a b e f c g h
--- PASS: TestPreTraversal (0.00s)
PASS
*/
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
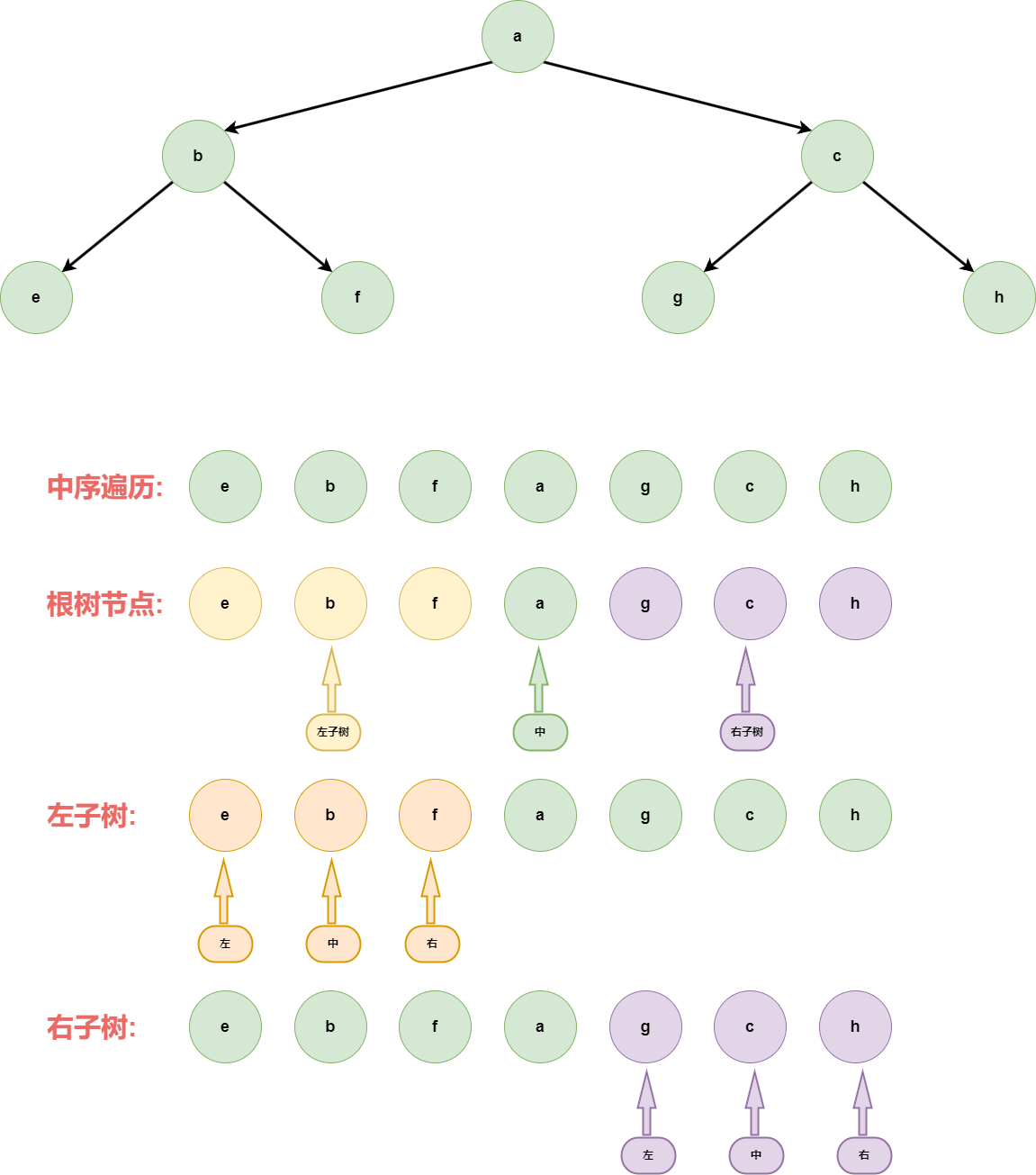
# 中序遍历
中序遍历(In-order Traversal): 任何子树的处理顺序都是,先左子树、再头节点、然后右子树
代码实现
func InTraversal(root *TreeNode) { // 中序遍历树节点
if root == nil {
return
}
InTraversal(root.Left) // 先中序遍历树的左子树
fmt.Printf("%s ", root.Value) // 再处理自身节点
InTraversal(root.Right) // 最后中序遍历树的右子树
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
测试
func TestInTraversal(t *testing.T) {
root := &TreeNode{Value:"a"}
root.Left = &TreeNode{Value:"b"}
root.Right = &TreeNode{Value:"c"}
root.Left.Left= &TreeNode{Value:"e"}
root.Left.Right= &TreeNode{Value:"f"}
root.Right.Left= &TreeNode{Value:"g"}
root.Right.Right= &TreeNode{Value:"h"}
InTraversal(root)
}
/* 测试结果
=== RUN TestInTraversal
e b f a g c h
--- PASS: TestInTraversal (0.00s)
PASS
*/
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
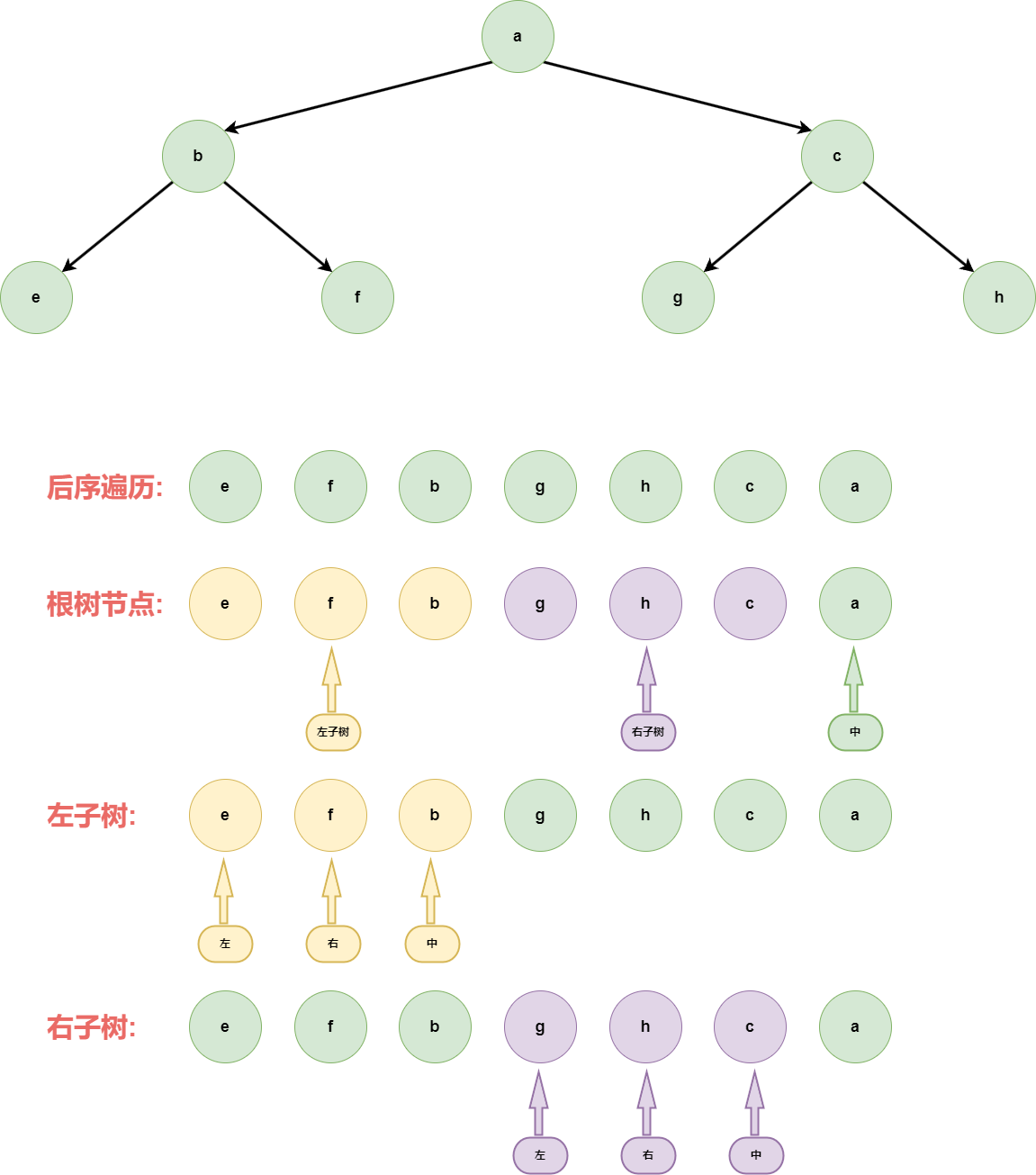
# 后序遍历
后序遍历(Post-order Traversal): 任何子树的处理顺序都是,先左子树、再右子树、然后头节点
代码实现
func PostTraversal(root *TreeNode) {// 后序遍历树节点
if root == nil {
return
}
PostTraversal(root.Left) // 先后序遍历树的左子树
PostTraversal(root.Right) // 再后序遍历树的右子树
fmt.Printf("%s ", root.Value) // 最后先处理自身节点
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
测试
func TestPostTraversal(t *testing.T) {
root := &TreeNode{Value:"a"}
root.Left = &TreeNode{Value:"b"}
root.Right = &TreeNode{Value:"c"}
root.Left.Left= &TreeNode{Value:"e"}
root.Left.Right= &TreeNode{Value:"f"}
root.Right.Left= &TreeNode{Value:"g"}
root.Right.Right= &TreeNode{Value:"h"}
PostTraversal(root)
}
/* 测试结果
=== RUN TestPostTraversal
e f b g h c a
--- PASS: TestPostTraversal (0.00s)
PASS
*/
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
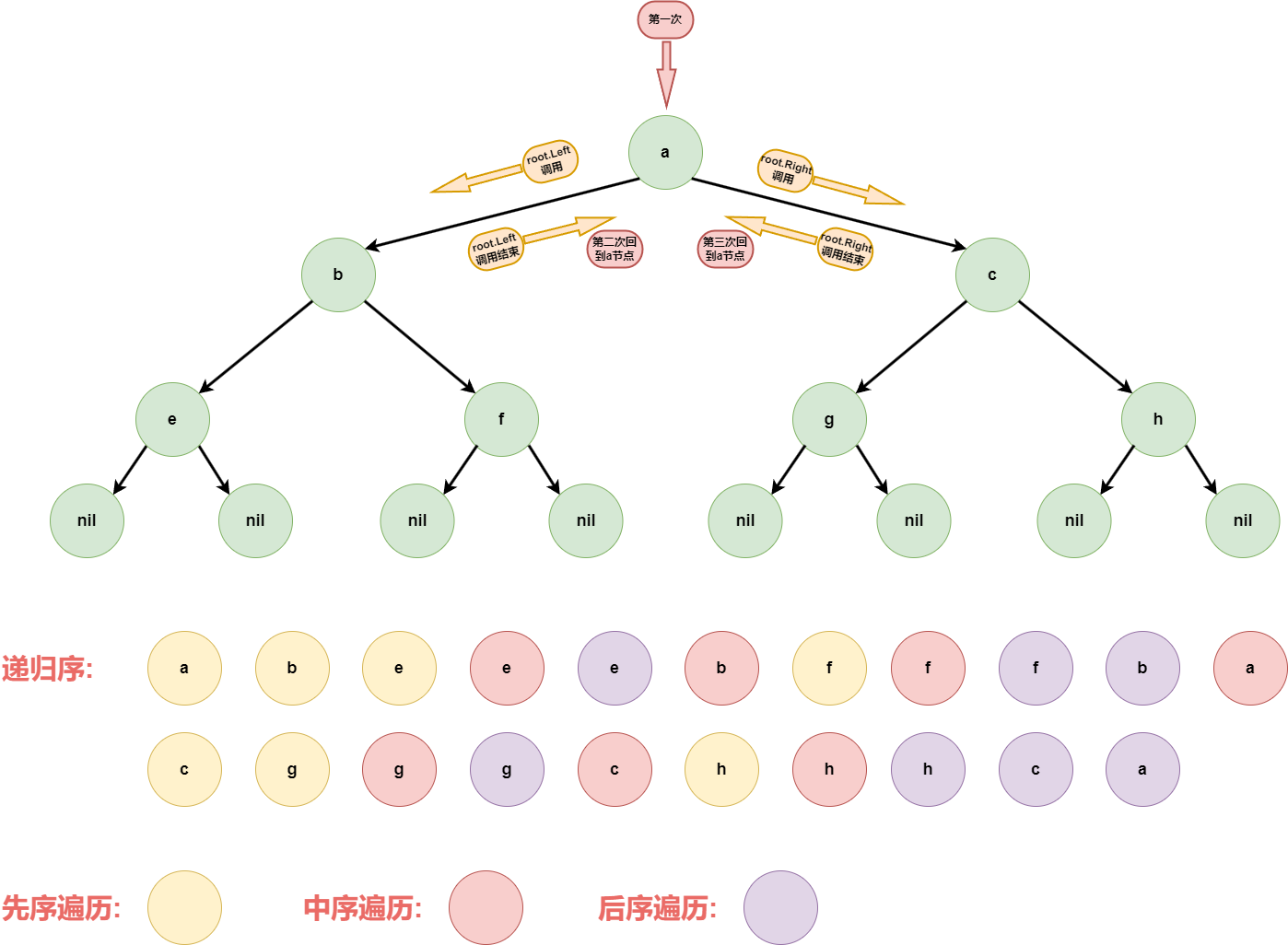
# 递归序
我们对二叉树的遍历实际上是对递归序的一种运用,使用递归遍历二叉树时,每个节点都会到三次,代码如下所示:
func RecursiveTreeNode(root *TreeNode) {
if root == nil {
return
}
// 1. 第一次来到当前节点 root
RecursiveTreeNode(root.Left)
// 2. 第二次来到当前节点 root
RecursiveTreeNode(root.Right)
// 3. 第三次来到当前节点 root
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
- 第一次到达该节点就打印,即为先序遍历
- 第二次到达该节点就打印,即为中序遍历
- 第三次到达该节点就打印,即为后序遍历